AI-enabled Decision Support Systems

Decision Support Systems
Decision support systems (DSS) are computer-based systems that utilize the information and knowledge about a system to assist decision makers make informed decisions. Modern DSS systems consist of different types of modeling techniques, database management, and data summarization and visualization tools. They enable users to run scenarios reflecting a future change in the inputs or management conditions of the system and evaluate their impacts on system performance.
Design and Main Components
Effective design and development of a DSS is a multidisciplinary process which requires deep understanding of relevant modeling techniques that are used for simulating the different components of a system. The main inputs, processes, and decision variables are represented in form of model parameters and their interactions are accounted for through a set of mathematical equations or data-driven models. The users should be able to define different scenarios regarding future system conditions or decision variable by setting new values for inputs and model parameter through an effective User Interface (UI).
Example
DataOrbs Inc. has been active in the development of novel system modeling and analysis techniques as well as their implementations and incorporation into powerful model-based decision tools. For example, the water quality and crop yield production DSS, developed by DataOrbs Inc. (see limited version) allows for evaluation of the impact of different weather and management scenarios on water quality and crop yield production in agricultural systems.
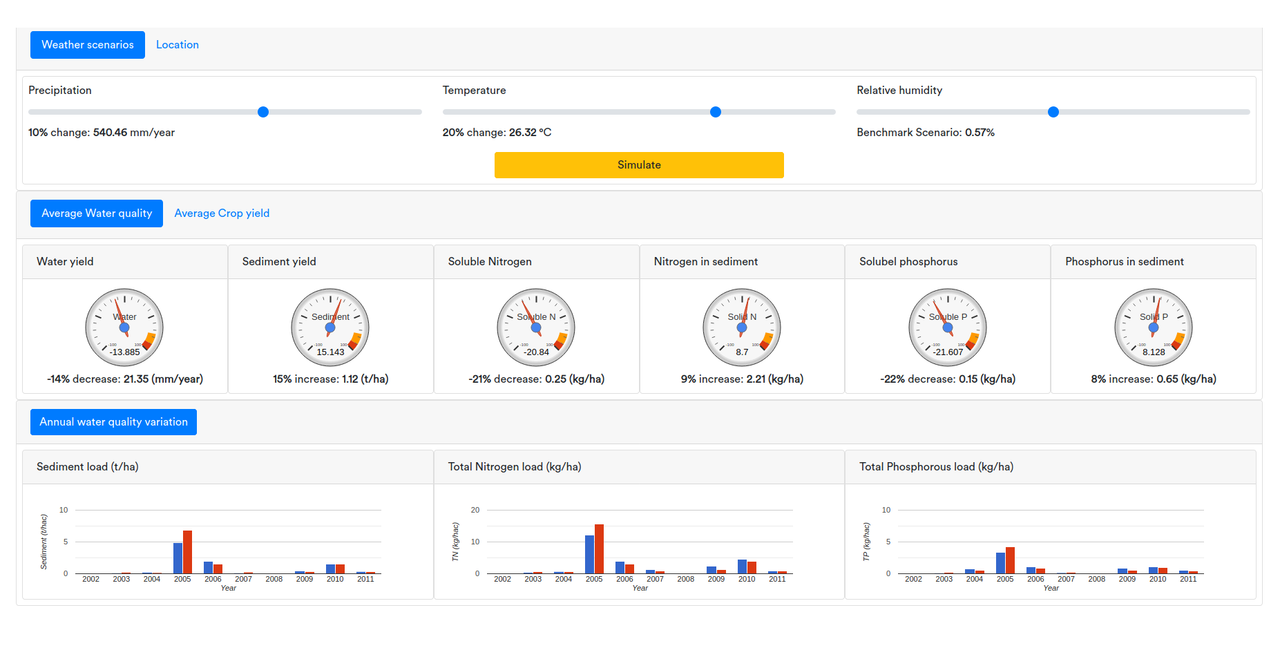
Weather data are input through an AI-enabled system, capable of finding representative values from public weather databases or generate them using a set of data-driven models. The modeling of important physical, biological, and plant-related processes governing rainfall-runoff generations, soil erosion and plant growth are simulated through a set of modeling tools (well-known watershed and farm simulation models like the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) or APEX - Agricultural Policy/Environmental eXtender) and data-driven models.
A set of derivative-based and evolutionary-based optimization algorithm can also be employed to generate a set of decision alternatives that respect a set of system constraints. The generated decision alternatives can be further evaluated using a set of quantitative and qualitative criteria by the decision makers.
